cho tam giác ABC sao cho có G là trọng tâm . Gọi H là chân đường đường cao hạ từ A sao cho \(\overrightarrow{BH}=\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{HC}\), Điểm M di động nằm trên BC sao cho \(\overrightarrow{BM}=x\overrightarrow{BC}\) . tìm x sao cho độ dài của vecto \(\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{GC}\)đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất .
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Gọi A là trọng tâm tam giác ABC. AB = GB-GA = ỊmB-|kA 3 3 = |(AK-BM) = |(Ó-Ĩ) Ta có BC = GC - GB = (-GA - GB) - GB =-GA-2GB = AG + 2BG Chú ý: A là trọng tâm AABC thì GA + AB + AC = õ.

Dựng hình bình hành \(AGCE\). Ta có: \(\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{GC}=\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{AE}=\overrightarrow{ME}\)
Kẻ \(EF\perp BC\left(F\in BC\right)\). Khi đó: \(\left|\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{GC}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{ME}\right|=ME\ge EF\)
Do đó: \(\left|\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{GC}\right|\) nhỏ nhất khi \(M\equiv F\)
Gọi \(P\) là trung điểm \(AC,Q\) là hình chiếu vuông góc của \(P\) lên
Khi đó \(P\) là trung điểm \(GE\) nên \(BP = \dfrac{3}{4}BE \)
Ta có: \(\Delta BPQ\sim\Delta BEF\Rightarrow\)\(\dfrac{{BQ}}{{BF}} = \dfrac{{BP}}{{BE}} = \dfrac{3}{4}\) hay \(\overrightarrow {BF} = \dfrac{4}{3}\overrightarrow {BQ} \)
Mặt khác, \(\overrightarrow {BH} = \dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {HC} \)
$PQ$ là đường trung bình \(\Delta AHC\) nên $Q$ là trung điểm $HC$ hay \(\overrightarrow {HQ} = \dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {HC} \)
Suy ra: \(\overrightarrow {BQ} = \overrightarrow {BH} + \overrightarrow {HQ} = \dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {HC} + \dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {HC} = \dfrac{5}{6}\overrightarrow {HC} = \dfrac{5}{6}.\dfrac{3}{4}\overrightarrow {BC} = \dfrac{5}{8}\overrightarrow {BC} \)
Do đó: \(\overrightarrow {BF} = \dfrac{4}{3}\overrightarrow {BQ} = \dfrac{5}{6}\overrightarrow {BC} \)

\(\overrightarrow{GB}=-\frac{1}{3}\left(\overrightarrow{BA}+\overrightarrow{BC}\right)=\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AB}-\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{BC}\)
\(=\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AH}+\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{HB}-\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{BC}=\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AH}+\frac{1}{3}.\frac{3}{4}\overrightarrow{BC}-\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{BC}\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{GB}=\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AH}-\frac{1}{12}\overrightarrow{BC}\)
\(\overrightarrow{MA}=\overrightarrow{MH}+\overrightarrow{HA}=\left(\frac{1}{4}-x\right)\overrightarrow{BC}-\overrightarrow{AH}\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{GB}=\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)\overrightarrow{BC}-\frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AH}\)
Đặt \(T=\left|\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{GB}\right|=\left|\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)\overrightarrow{BC}-\frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AH}\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow T^2=\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)^2.BC^2+\frac{4}{9}AH^2\ge\frac{4}{9}AH^2\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\frac{1}{3}-x=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{3}\)

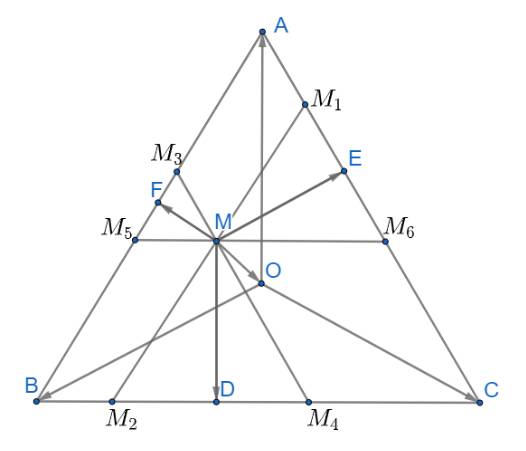
\(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OD} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OE} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OF} } \right)\)
Qua M kẻ các đường thẳng \({M_1}{M_2}//AB;{M_3}{M_4}//AC;{M_5}{M_6}//BC\)
Từ đó ta có: \(\widehat {M{M_1}{M_6}} = \widehat {M{M_6}{M_1}} = \widehat {M{M_4}{M_2}} = \widehat {M{M_2}{M_4}} = \widehat {M{M_3}{M_5}} = \widehat {M{M_5}{M_3}} = 60^\circ \)
Suy ra các tam giác \(\Delta M{M_3}{M_5},\Delta M{M_1}{M_6},\Delta M{M_2}{M_4}\) đều
Áp dụng tính chất trung tuyến \(\overrightarrow {AM} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} } \right)\)(với M là trung điểm của BC) ta có:
\(\overrightarrow {ME} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right);\overrightarrow {MD} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right);\overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
Ta có: các tứ giác \(A{M_3}M{M_1};C{M_4}M{M_6};B{M_2}M{M_5}\) là hình bình hành
Áp dụng quy tắc hình bình hành ta có
\(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_3}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_4}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MA} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MC} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OA} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OB} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OC} } \right)} \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {3\overrightarrow {MO} + \left( {\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} } \right)} \right) = \frac{3}{2}\overrightarrow {MO} \) (đpcm)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{3}{2}\overrightarrow {MO} \)